What Engineers Notice About Joint Pain (Most Don’t)
Joint pain is a common complaint affecting millions worldwide, yet few consider the unique perspective engineers bring to understanding this condition. Engineers are trained to analyze systems, identify root causes, and optimize performance—skills that can offer fresh insights into the complexities of joint pain. Unlike typical approaches that focus solely on symptoms, engineers examine the mechanics behind joint function and dysfunction, uncovering factors often overlooked by others.
How Engineers Analyze Joint Pain Differently
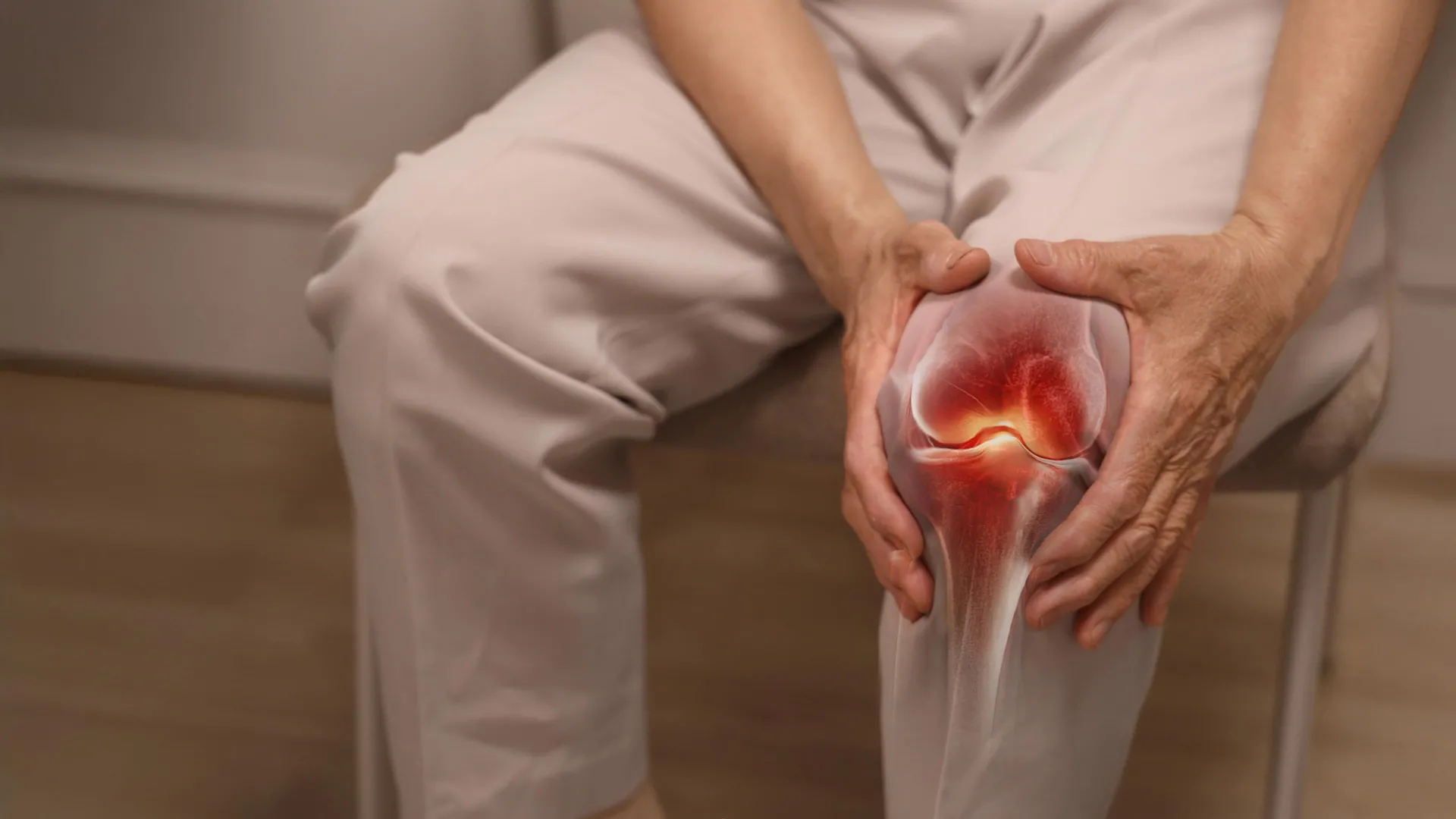
Engineers approach joint pain by treating the human body as a complex mechanical system. They observe how forces, motion, and structural integrity influence joint health. This analytical mindset leads to several key observations:
– Load Distribution and Stress Points: Engineers notice how uneven load distribution across joints can accelerate wear and tear. For example, improper gait or posture can place excessive stress on certain areas, leading to inflammation and pain.
– Material Fatigue in Biological Tissues: Just as materials fatigue under repetitive stress, cartilage and ligaments degrade over time with continuous strain. Engineers recognize patterns of microdamage accumulation that contribute to chronic joint issues.
– Alignment and Structural Integrity: Misalignment in bones or joints disrupts normal biomechanics. Engineers use principles of alignment to understand how deviations cause abnormal joint movement and pain.
– Systemic Interactions: Engineers consider how interconnected systems affect joint health. Muscle weakness, nerve function, and even external factors like footwear impact joint mechanics.
This comprehensive, systems-based perspective helps identify root causes rather than merely treating symptoms, enabling more effective interventions.
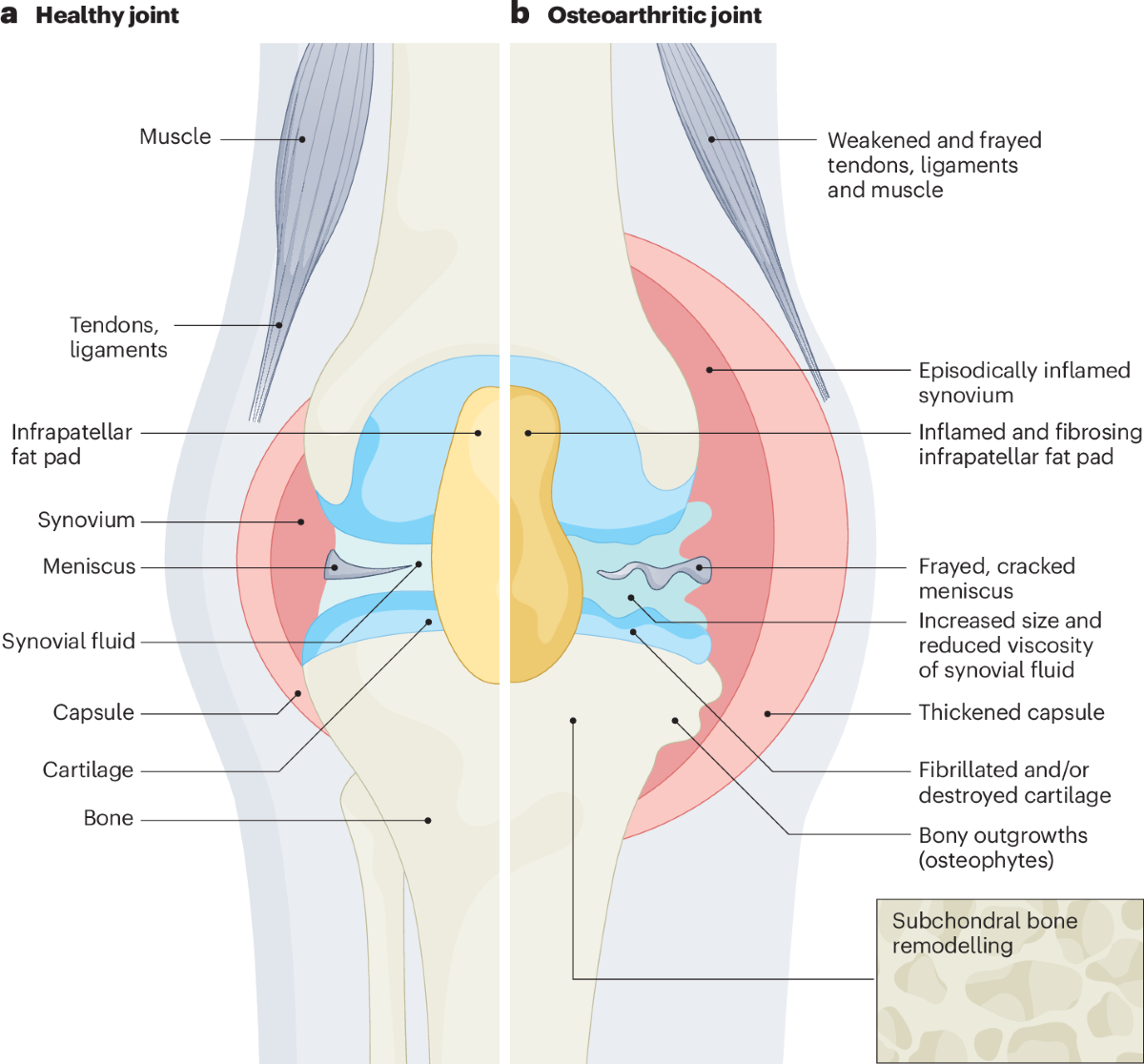
Common Causes of Joint Pain Identified Through Engineering Principles

By applying engineering concepts, several common causes of joint pain become clearer:
- Mechanical Overload: Excessive force beyond a joint’s capacity leads to damage. This can result from heavy lifting, repetitive motions, or sudden trauma.
-
Wear and Tear (Osteoarthritis): Continuous mechanical stress causes cartilage breakdown, similar to how machine parts wear down with use.
-
Poor Biomechanics: Faulty movement patterns, such as overpronation or improper lifting techniques, increase joint stress.
-
Inflammation and Swelling: Engineers understand that inflammation changes the mechanical environment of joints, increasing pressure and reducing mobility.
-
Structural Abnormalities: Congenital or acquired deformities alter joint mechanics, causing pain and dysfunction.
Understanding these causes through an engineering lens allows for targeted strategies to reduce joint stress and promote healing.
Practical Tips for Managing Joint Pain Inspired by Engineering Insights
Leveraging their analytical skills, engineers suggest several practical approaches to manage and prevent joint pain:
– Optimize Movement Patterns: Just as machines require proper alignment, humans benefit from correct posture and movement. Physical therapy and ergonomic assessments can help achieve this.
– Strengthen Supporting Structures: Building muscle strength around joints distributes loads more evenly, reducing stress on vulnerable areas.
– Use Appropriate Supportive Devices: Braces, orthotics, and proper footwear can correct alignment issues and absorb shock.
– Incorporate Rest and Recovery: Allowing time for tissues to repair prevents fatigue damage, similar to maintenance schedules in machinery.
– Monitor and Adjust Activity Levels: Avoiding repetitive overload and gradually increasing activity intensity helps maintain joint health.
By applying these principles, individuals can improve joint function and reduce pain over time.
Conclusion
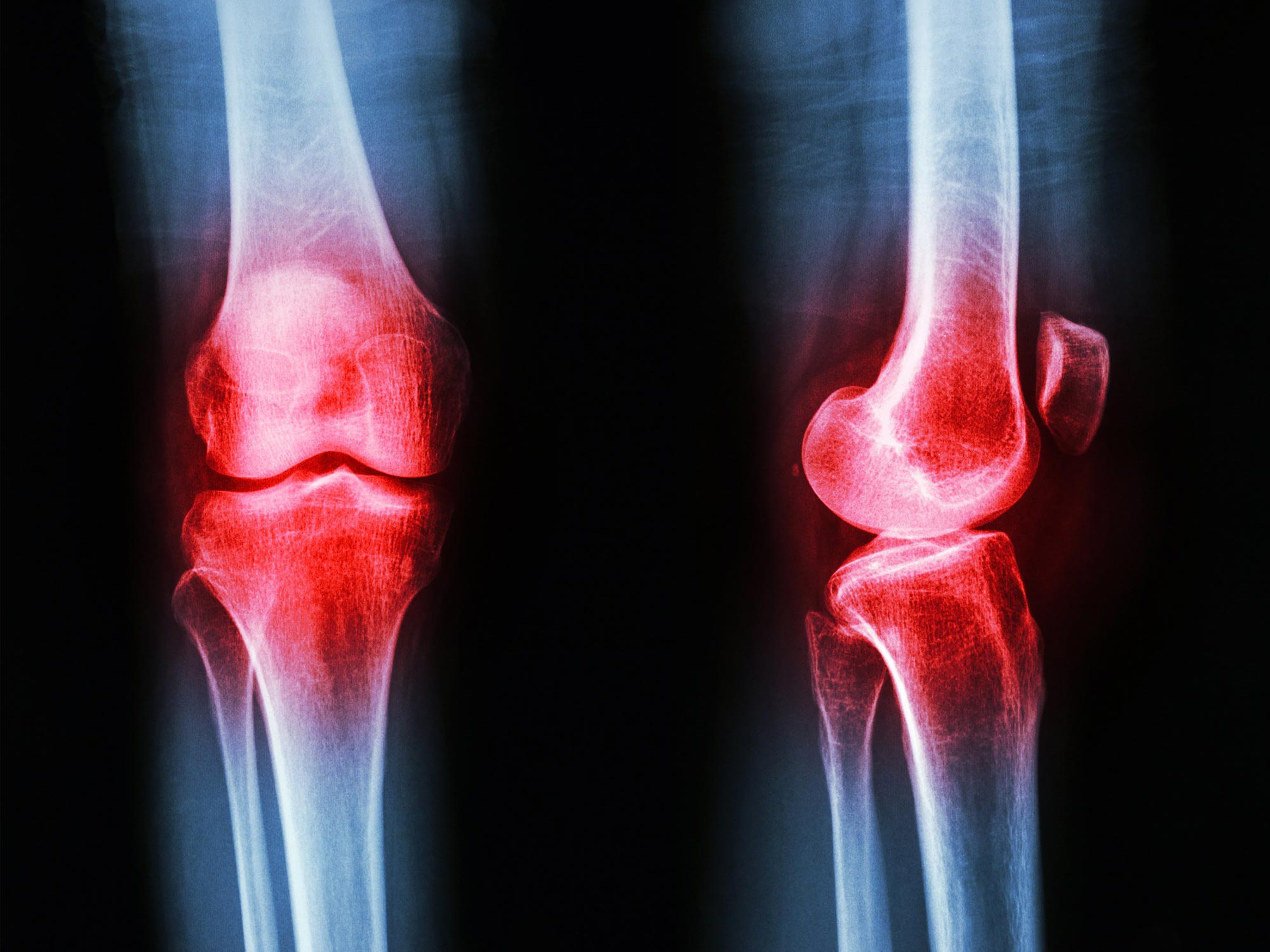
Engineers bring a unique and valuable perspective to understanding joint pain by analyzing the mechanical and systemic factors involved. Their approach goes beyond symptom management to uncover root causes and optimize joint health through practical, evidence-based strategies. If you’re struggling with joint pain, consider adopting an engineer’s mindset: assess your movement, strengthen your support systems, and prioritize proper alignment. For personalized guidance and effective solutions, consult with healthcare professionals who incorporate biomechanical principles into their care. Take control of your joint health today and move towards a pain-free future.









