Neck Pain Explained: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatments
Understanding Neck Pain: Causes and Symptoms
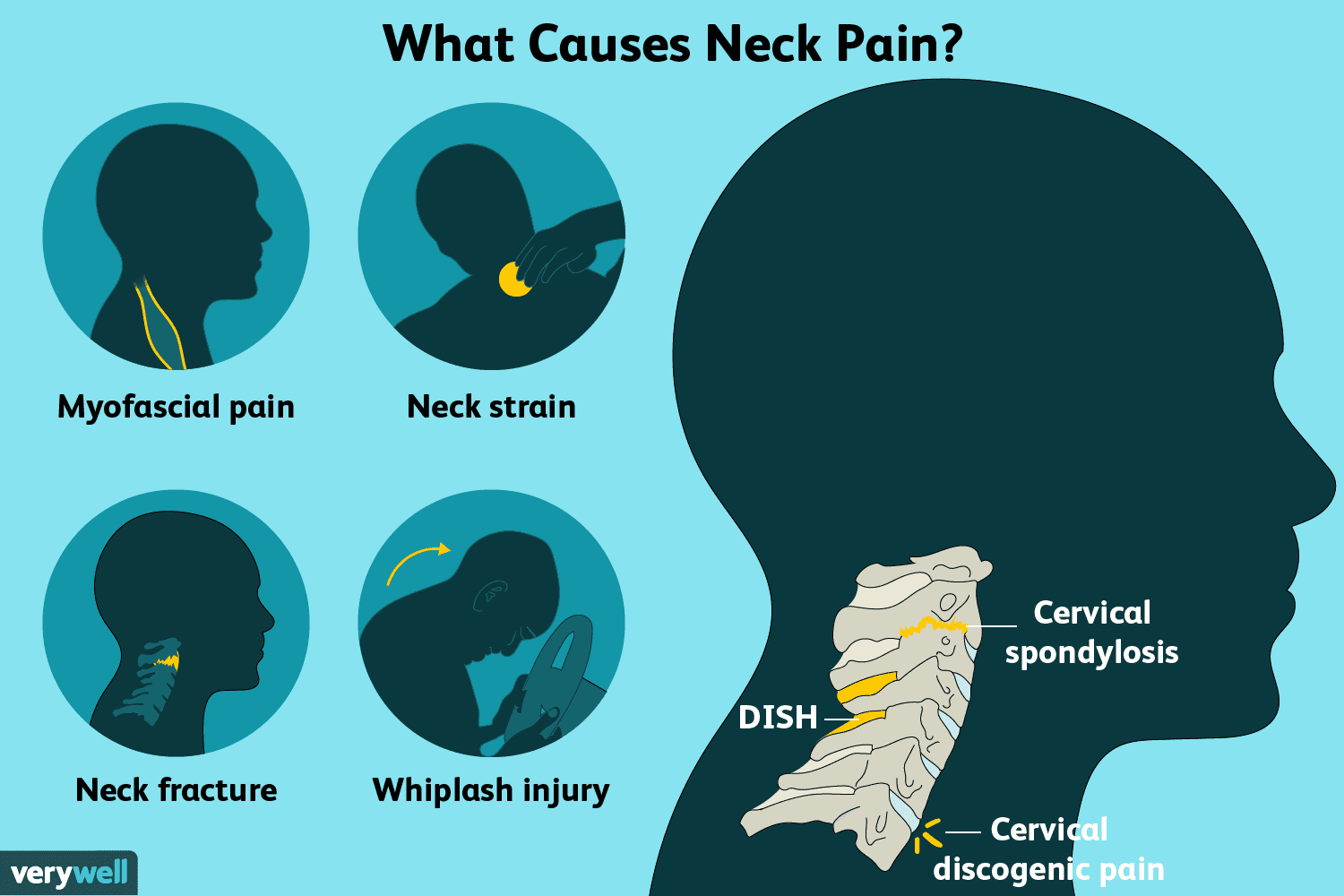
Neck pain is a widespread condition that affects millions of people worldwide, ranging from mild discomfort to severe, debilitating pain. The neck plays a crucial role in supporting the head and enabling a wide range of movements such as turning, tilting, and nodding. Because of its constant use and complex structure, the neck is susceptible to various issues that can cause pain.
The cervical spine, which forms the neck, consists of seven vertebrae starting from the base of the skull down to the shoulders. These vertebrae are cushioned by soft, gel-like intervertebral discs that act as shock absorbers. Surrounding the spine are muscles, ligaments, and tendons that provide stability and flexibility. The spinal cord runs through the vertebrae, with nerve roots branching out to different parts of the body, transmitting signals between the brain and muscles.
Neck pain symptoms can vary widely. Some individuals experience a persistent dull ache, while others may feel sharp, stabbing, or burning sensations. Additional symptoms often include headaches, muscle tightness, numbness, or tingling sensations radiating into the arms. These symptoms can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life.
Common Causes of Neck Pain
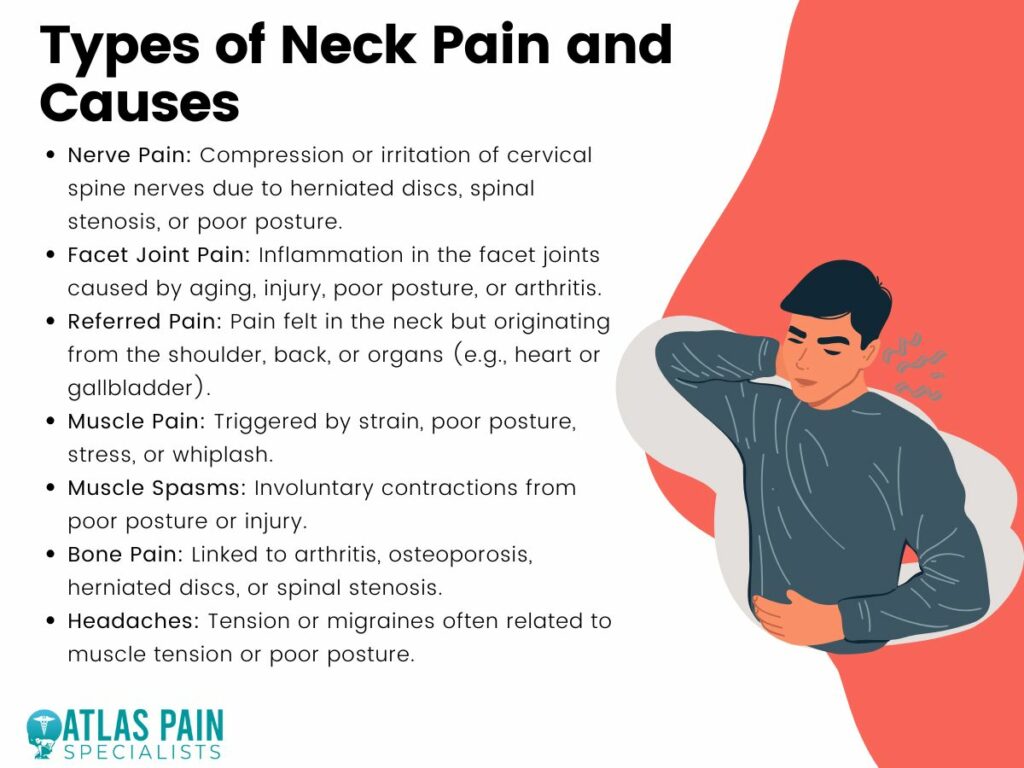
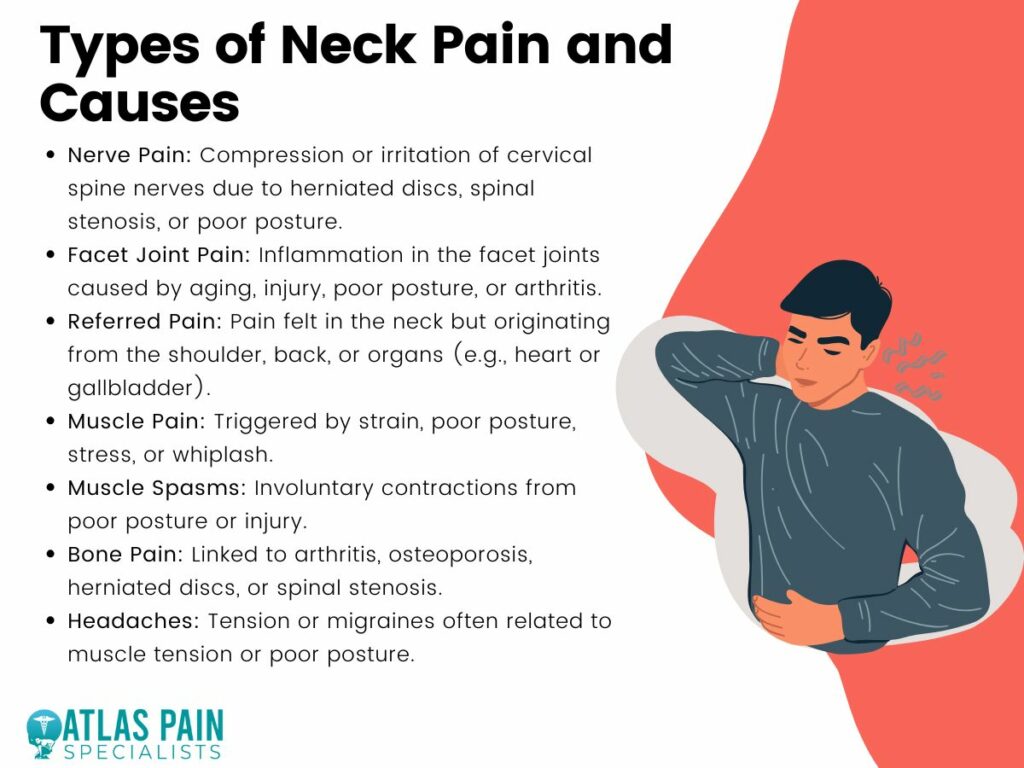
Several factors can contribute to neck pain, including:
– Degenerative Disc Disease: Over time, the intervertebral discs can deteriorate, losing their cushioning ability and causing pain.
– Arthritis: Osteoarthritis can affect the cervical spine, leading to inflammation and stiffness.
– Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal compresses nerves, resulting in pain and neurological symptoms.
– Muscle Strain: Poor posture, repetitive movements, or sudden awkward positions can strain neck muscles.
– Injuries: Trauma from accidents, falls, or sports can cause sprains, fractures, or dislocations.
– Other Causes: Less common causes include infections like meningitis or serious conditions such as tumors.
Age, lifestyle habits, and occupational factors also play a role in the development of neck pain. For example, prolonged computer use without ergonomic adjustments often leads to muscle tension and discomfort.
Types of Neck Pain: Acute vs. Chronic and Axial vs. Radicular
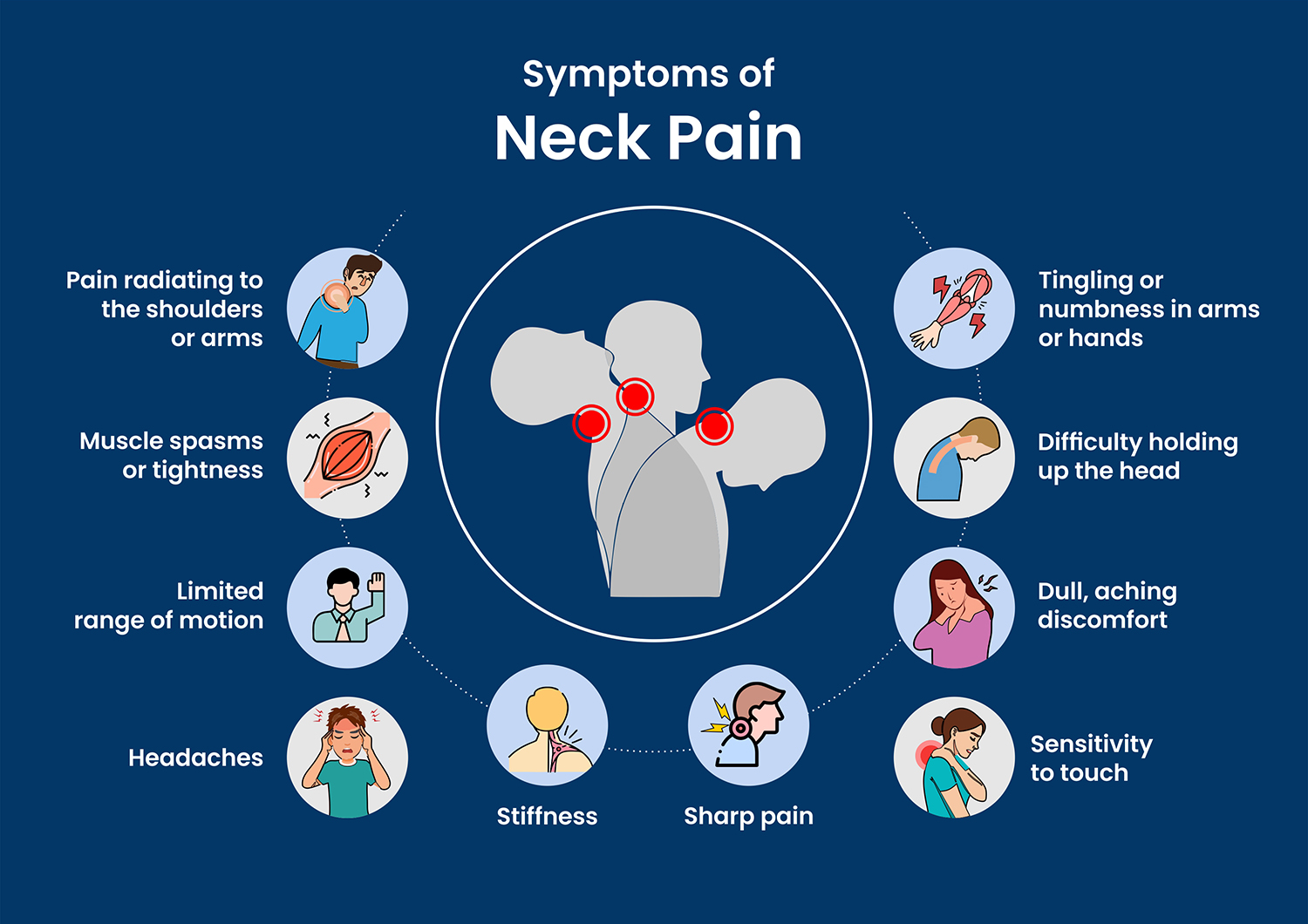
Understanding the type of neck pain you are experiencing can help guide treatment decisions.
Acute Neck Pain occurs suddenly, often due to injury or strain, and typically resolves within a few days to weeks. Common causes include sleeping in an awkward position or muscle overuse.
Chronic Neck Pain persists for more than three months and may be associated with underlying conditions such as arthritis or nerve compression. Chronic pain can be more challenging to manage and may require comprehensive treatment.
In addition to duration, neck pain can be categorized by its location and nature:
– Axial Neck Pain: This pain is localized to the neck and surrounding soft tissues. It is often described as a dull ache or stiffness.
– Radicular Neck Pain: This type results from nerve root irritation or compression, causing pain that radiates from the neck into the shoulders, arms, or hands. Symptoms may include numbness, tingling, or muscle weakness.
When to Seek Medical Attention

While many cases of neck pain improve with self-care, certain symptoms warrant prompt medical evaluation:
– Severe neck pain following trauma or injury
– Persistent pain lasting more than a week
– Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the arms or hands
– Difficulty swallowing or breathing
– Fever accompanied by neck stiffness and headache
– Pain that disrupts sleep or daily activities
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Effective Treatments for Neck Pain

Treatment options for neck pain depend on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms. Many cases respond well to conservative management, while others may require more advanced interventions.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Adjustments

For minor neck pain, the following measures can provide relief:
– Over-the-Counter Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can reduce pain and inflammation.
– Cold and Heat Therapy: Applying ice packs during the first 48 to 72 hours helps reduce swelling, followed by heat therapy to relax muscles.
– Gentle Exercises: Slowly moving the neck through its range of motion can prevent stiffness.
– Ergonomic Improvements: Adjusting computer screens to eye level, using hands-free devices for phones, and maintaining good posture reduce strain.
– Massage Therapy: Massaging tense muscles can alleviate discomfort.
Medical Treatments

If home remedies are insufficient, medical professionals may recommend:
– Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises and manual therapy improve strength and flexibility.
– Prescription Medications: Muscle relaxants or stronger pain relievers may be prescribed.
– Injections: Corticosteroid injections can reduce inflammation around nerve roots.
– Surgery: Reserved for severe cases involving nerve compression or spinal instability, surgical options include removing bone spurs, herniated discs, or spinal fusion.
Post-surgical rehabilitation is essential to restore function and prevent recurrence.
Preventing Neck Pain: Tips for a Healthy Neck

Prevention is key to avoiding neck pain or minimizing its impact. Consider the following strategies:
– Maintain good posture, especially when sitting for extended periods.
– Take frequent breaks to stretch and move during desk work.
– Use supportive pillows and avoid sleeping with multiple pillows stacked.
– Stay physically active to strengthen neck and back muscles.
– Avoid lifting heavy objects improperly.
– Manage stress through relaxation techniques, as tension can contribute to muscle pain.
Potential Complications of Untreated Neck Pain

Ignoring neck pain can lead to several complications, including:
– Reduced productivity due to pain-related disability
– Nerve damage causing chronic pain or weakness
– Psychological effects such as anxiety and depression
– Decreased physical activity leading to weight gain and other health issues
Early intervention helps prevent these adverse outcomes.
Conclusion
Neck pain is a common yet complex condition that can significantly affect your daily life. Understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms, and knowing when to seek medical care are essential steps toward effective management. Whether your neck pain is acute or chronic, axial or radicular, there are numerous treatment options available to help you find relief and restore function. Don’t let neck pain limit your life—consult a healthcare professional today to develop a personalized treatment plan and take the first step toward a pain-free neck.